What Is Market Segmentation?
Organizing
potential customers into groups or segments with comparable demands and
responses to marketing actions is referred to as market segmentation in
marketing. Market segmentation helps businesses to target various customer
groups who view the entire worth of certain goods and services in a variety of
ways.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Market
segmentation is to pinpoint specific customer groups so that merchandise
and branding may be tailored to appeal to them.
- There are
many different ways to segment markets, including geographically,
demographically, or behaviorally.
- By
identifying the items that are most likely to capture a portion of a
target market and the most effective channels for marketing and
distributing those products, market segmentation aids businesses in
reducing risk.
- A
corporation may then concentrate its resources on activities that are
expected to yield the highest profits when risk is reduced and clarity regarding the marketing and delivery of a product is increased. - A
company's demographic reach can be expanded by market segmentation, and it
can also lead to the discovery of goods or services they had not
previously thought about.
how to segment markets
Three
factors may often be used by businesses to distinguish between various market
segments:
1. Homogeneity, or a segment's common
requirements
2. Distinction, or being unique
from other groups
3. Reaction, or an equal
reaction to the market
For
instance, a firm that sells sports footwear may have market segments for
long-distance runners and basketball players. Basketball players and marathon
runners react to commercials quite differently as separate groups. The firm
that makes sports footwear is better equipped to promote its branding by having
a thorough understanding of these various market niches.
Market
segmentation is a development of market research that aims to pinpoint specific
customer groups in order to develop goods and brands that appeal to the group. Market
segmentation tries to lower risk by determining which goods have the best
chance of capturing a share of a target market and determining the best method
to bring those products to market. As a result, the company is able to increase
overall efficiency by focusing its limited resources on projects that have the
best rate of return on investment (ROI).
By
concentrating scarce resources on initiatives that yield the highest return on
investment, market segmentation enables a business to boost its overall
efficiency (ROI).
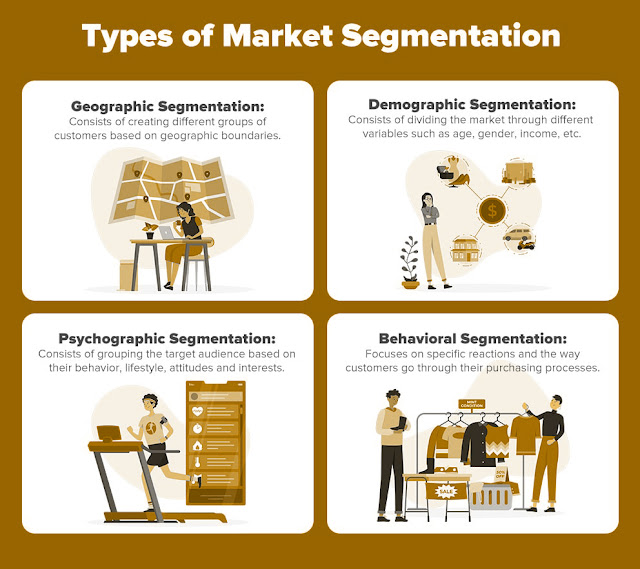
Types of Market Segmentation
The four main categories of market segmentation are as follows. One kind, however, may often be divided into individual and organizational segments. There are five typical categories of market segmentation listed below.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic
segmentation is one of the simple, regularly used methods for market
segmentation. It entails segmenting the market based on factors like as age,
income, gender, race, education, and occupation of the target market. According
to this market segmentation technique, people with comparable demographics will
have comparable wants.
Example: The market segmentation
plan for a new video game system may show that young men with discretionary
income make up the majority of its players.
Firmographic Segmentation
Demographic
segmentation and firmographic segmentation are the same. However, instead of
analyzing individuals, this strategy looks at organizations and look. Demographic
segmentation and firmographic segmentation are the same ideas. This technique
examines organizations rather than people and considers a company's personnel
count, clientele, number of locations, or yearly income. at the number of
workers, customers, offices, or yearly income of a corporation.
Example: While pursuing smaller
businesses with a set price, a more straightforward solution, a corporate
software vendor may approach a global company with a more comprehensive,
configurable suite.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic
segmentation is technically a subset of demographic segmentation. This strategy
organizes clients according to their actual locations on the basis that it's
likely that residents in the same region will have comparable wants. For larger
businesses looking to diversify into new branches, offices, or locations, this
technique works better.
Example: In comparison to their
Southwest locations Pacific Northwest sites could provide more rain gear.
Behavioral Segmentation
Consumer
behavior, consumer activities, and customer decision-making patterns are all
important components of behavioral segmentation. Based on their prior
interactions with markets and products, this strategy divides customers into
categories. This strategy makes the assumption that consumers' past spending
patterns predict what they would likely buy in the future, even if purchasing
patterns might vary over time or in reaction to external factors.
Example: Craft beer is typically
more popular among millennial customers than major brands, according to
historical data.
Psychographic
Segmentation
Psychographic
segmentation, often the most complex market segmentation strategy, seeks to
categorize customers based on their lifestyle, personality, attitudes, and
interests. This may be more difficult to do since these features (1) change
quickly and (2) lack readily available objective data. However, because it
organizes individuals based on internal motivators rather than external data
points, this strategy may produce the best market segment outcomes.
Example: A fitness gear
business can focus on those who like participating in or watching a range of
sports.
Other less prominent
forms of segmentation include volume (i.e., how much a consumer spends),
use-related (i.e., a customer's level of loyalty), or other customer qualities
(i.e. how innovative or risk-favorable a customer is).
The Best Way to Choose Your Market Segment
There
isn't a single, generally acknowledged method for segmenting the market. Along
their market segmentation journey, businesses frequently ask themselves the
following questions in order to define their market segments.
Phase
I: Specifying goals and expectations
- What is
the aim or objective of market segmentation?
- What does the
business intend to learn by segmenting its market?
- Does the
business anticipate any potential market segments?
Phase
2: Establish Customer Segmentation
- Which
market categories do the rival businesses serve?
- What data
from the U.S. Census Bureau is available to the public that is pertinent
to our market?
- What
information do we need to gather, and how can we achieve that?
- Which of
the five market sector kinds should we divide up?
Phase
3: Analyze Potential Markets
- What
chances exist that our statistics won't accurately reflect the various
market segments?
- Why should
we favor one kind of clientele over another?
- What
long-term effects may select one market segment over another have?
- Which
market categories most closely resemble the "perfect client" for
the organization, and what is their ideal customer profile?
Phase
4: Create a segmentation plan
- How can
the business test its theories on a representative test market?
- What
attributes make a marketing segmentation plan effective?
- How will
the business know whether the plan is effective?
Phase
5: initiate and observe
- After the
market segmentation plan has been revealed, which important stakeholders
can offer feedback?
- What
obstacles to implementation are there, and how may they be removed?
- What
internal messaging should be used to announce the beginning of the
marketing campaign?
Market segmentation benefits
Implementing
marketing segmentation requires time and money. Successful marketing
segmentation strategies, however, can improve a company's long-term
profitability and health. Market segmentation offers a number of advantages,
such as;
- Increased
resource efficiency. Marketing segmentation enables management to
concentrate on particular consumer or demographic groups. Marketing
segmentation enables a targeted, precise strategy that frequently costs
less than a broad-reach approach, as opposed to attempting to offer items
to the whole market.
- Stronger
brand image. Management must think about how it wants to be regarded by a
certain set of individuals due to marketing segmentation. After
determining the market segment, management must select what message to
produce. The fact that this message is intended for a specific audience
suggests that a company's branding and marketing are more likely to be
extremely deliberate. This can also have the unintended consequence of
improving consumer interactions with the business.
- increased
chance of brand loyalty. Marketing segmentation increases the
possibilities of customers developing long-term relationships with a
company. Customers may appreciate more direct, human marketing methods
that foster feelings of inclusion, community, and belonging. Market
segmentation also boosts your chance of finding the ideal customer that
fits your product line and demography.
- greater market differentiation. A corporation may implement more effective customized
advertising methods thanks to marketing segmentation. This includes social
media marketing methods that target a certain age group, geographic
location, or habit.
- optimized
digital advertising targeting. Marketing segmentation helps a business to
execute more effective, tailored advertising campaigns. This covers
marketing strategies that use social media to target people of a certain
age, geography, or behavior.
Market division also takes place outside of the company. There has been a lot of study on reducing COVID-19 vaccine reluctance
and other health efforts utilizing market segmentation tactics.
Marketing strategy limitations.
Without
any possible drawbacks, the above advantages cannot be realized. Here are
several drawbacks to take into account before putting market segmentation
tactics into practice.
- higher
initial marketing costs. Marketing segmentation's long-term goal is
efficiency. To achieve this efficiency, though, businesses frequently have
to invest money upfront in order to gather information about their target
markets and client base.
- greater
chance of making mistakes. The assumption behind market segmentation is that
people with similar demographics have comparable needs. This could not
always be the situation. A corporation runs the danger of misidentifying
the needs, values, or motives of people within a particular community by
lumping them all together under the assumption that they have anything in
common.
- greater
dependence on trustworthy data. Market segmentation is only as reliable as the
evidence that underpins the assertions made. This necessitates paying
attention to the sources from which data is gathered. This entails being
aware of evolving patterns and instances in which market segmentation may
have changed from earlier surveys.
Examples of Market Segmentation
The
goods, marketing, and advertising that consumers utilize on a daily basis are
all examples of market segmentation. The success of auto manufacturers depends
on their ability to accurately identify market groups and develop products and
marketing strategies that appeal to those segments.
In
order to develop brand loyalty among younger customers, cereal companies
aggressively market to three or four market segments at once. They promote
conventional brands that appeal to older consumers and healthy brands to
consumers who are health-conscious.
Elite
athletes, regular gym attendees, fashion-conscious ladies, and middle-aged men
looking for quality and comfort in their shoes are just a few examples of the
market groups that a sports shoe maker could identify. In every situation, the
manufacturer's marketing knowledge of each market group helps it to create and
promote items with a high appeal more successfully than it might by trying to
appeal to a wider audience.
What Is Market
Segmentation?
Market
segmentation is a marketing technique that involves identifying certain customer
groups in order to deliver particular goods or product lines to them in a way
that appeals to their preferences.
Market segmentation: Why Is It Important?
Market
segmentation acknowledges that not all customers have the same preferences,
means of consumption, or demands. Market segmentation is significant because it
aims to make a company's marketing initiatives more strategic and focused, as
opposed to widely catering to all potential customers. A business may improve
its chances of making sales and being more resource-efficient by creating specialized
strategies for certain items with target consumers in mind.
What Kinds of Market Segmentation are there?
There
are several different types of segmentation, such as homogeneity, which
examines a segment's shared demands, distinctiveness, which examines how a
certain group differs from others, and response, which examines how specific groups
react to the market.
What Market Segmentation Techniques Are available?
Targeting a group may be done in a number of ways, such as by geography, by demographics like age or gender, by social class or lifestyle, or by behaviors like usage or reaction.
What Is a Market Segmentation Example?
After
doing research on its target market and ideal brand image, Crypto.com decided
to work with Matt Damon to promote both their platform and bitcoin trading.
Crypto.com's market segmentation targeted younger, more daring, and
risk-accepting people with images of space adventure and historical innovations
as backgrounds.
the conclusion
Companies utilize market segmentation as a method to divide up their potential clients into several groups. This makes it possible for the business to give the proper resources to each distinct group, enabling more precise targeting across a range of marketing efforts.

.jpg)


Post a Comment